.jpg)
Some people feel that WiFi 5 is already becoming outdated, so buying a WiFi 5 router would be a loss. On the other hand, some people simply believe that WiFi 6 has a higher level of prestige. Please allow me to provide an imperfect analogy by comparing WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 to smartphones. WiFi 6 can be likened to the iPhone 11, while WiFi 5 is comparable to the iPhone 7. Naturally, the iPhone 11 outperforms the iPhone 7 in all aspects.
However, does that mean the iPhone 7 is no longer usable? Certainly not. I have friends who still use the iPhone 6 with only 16GB of storage. I also have a Redmi 8, which has even lower performance, but it is still capable of tasks like chatting on WhatsApp, watching videos, and playing games like Honor of Kings. So, what am I trying to convey? I want to remind everyone not to forget the purpose of buying a router.
The primary purpose of buying a router is to address network issues, and the most crucial aspect of a router is network stability and good signal strength. It is not determined by the price or whether it is a WiFi 5 or WiFi 6 router.
As long as a router can meet your needs and resolve your network problems, then it is considered a good router.
1. What is WiFi 6?
WiFi 6 refers to the sixth-generation wireless local area network (WLAN) technology standard, also known as 802.11ax. It is the latest wireless networking technology standard that introduces several innovative features and improvements aimed at providing higher speeds, lower latency, and better device management capabilities. WiFi 6 technology builds upon previous WiFi standards but with significant enhancements and optimizations to cater to the increasing number of wireless devices and data demands in modern homes, offices, and public environments. By utilizing technologies such as Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO), Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), and Target Wake Time (TWT), WiFi 6 achieves higher throughput, more stable connections, and lower power consumption. This makes WiFi 6 an ideal choice for meeting the needs of future smart devices and high-capacity data transmissions.
Correct, WiFi 6 is also known as 802.11ax, which represents the new generation of Wi-Fi standards. On October 4, 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced the renaming of 802.11ax to WiFi 6.
The name changes for previous generations of Wi-Fi are as follows: 802.11ac became WiFi 5, and 802.11n became WiFi 4.
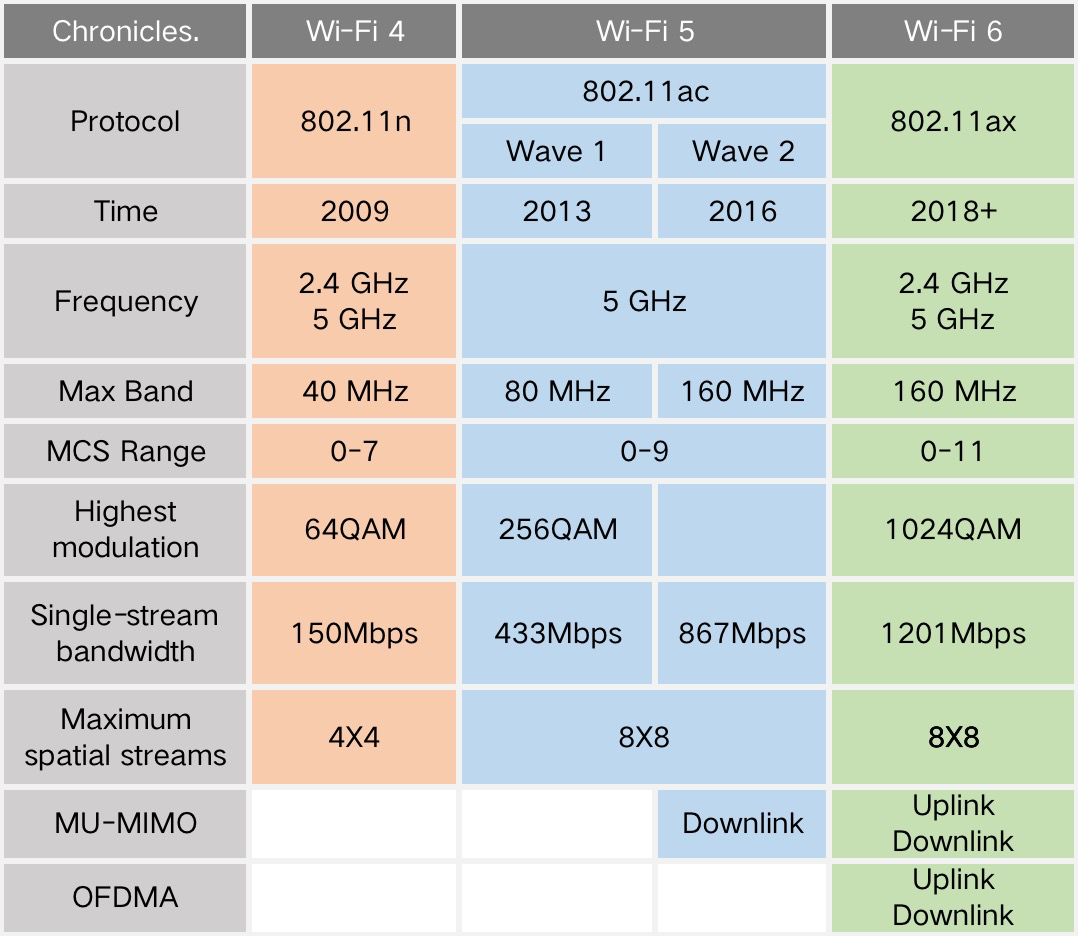
2、How fast is WiFi 6? And how much faster is it compared to WiFi 5?
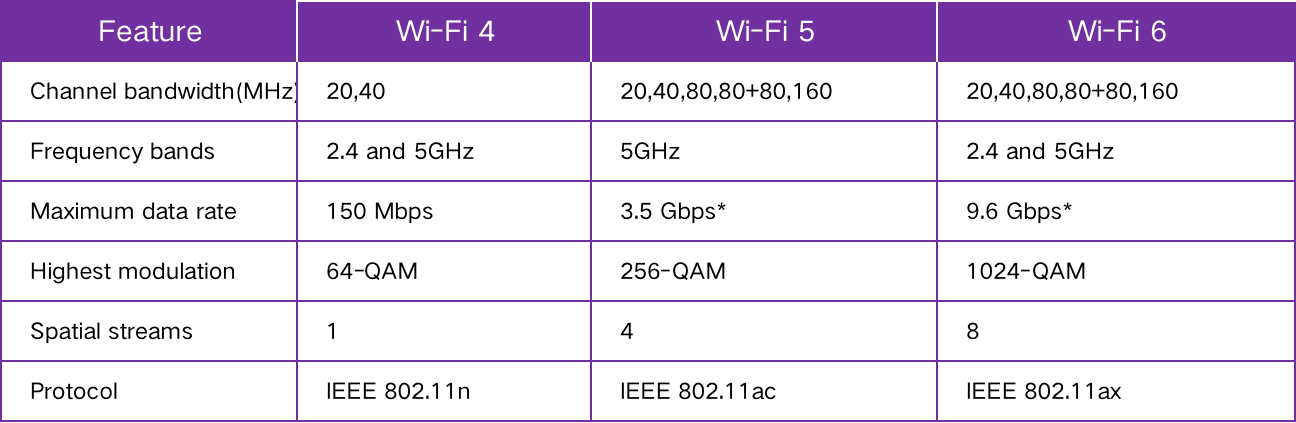
According to reports, the maximum data transfer rate of the latest generation WiFi 6 can reach up to 9.6Gbps, which translates to a theoretical transfer speed of 1.2GB/s. In comparison, WiFi 5 has a maximum data transfer rate of 3.5Gbps and a theoretical speed of 866MB/s, while WiFi 4 has a theoretical speed limited to 150Mb/s.
Correct, the more realistic answer is that these speeds are theoretical maximum values and are difficult to achieve in real-life scenarios. In practical situations, WiFi performance can vary depending on factors such as the range between the wireless access points and devices, the presence of obstacles, the quality of other signals in the air, and radio interference. These factors can affect the actual performance of WiFi in everyday life.
Indeed, the speed improvement offered by WiFi 6 remains significant. While the 9.6 Gbps speed may not be achievable by a single device alone, it can be distributed among all devices within the network. This means that each device potentially has access to faster speeds. The increased overall network capacity of WiFi 6 allows for better performance and faster data transfers across multiple devices simultaneously.

3、The issues with WiFi 5
WiFi 5 (802.11ac) brought many improvements when it was introduced, but it also has some issues.
Network congestion: With the increasing number of devices using WiFi connections, especially in high-density environments, WiFi 5 networks can face spectrum congestion and interference. This can lead to weakened signals, decreased speeds, and unstable connections.
Handling multiple devices: While WiFi 5's Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) technology allows for simultaneous data transmission from multiple devices, performance may suffer when a large number of devices are connected at the same time. In homes or offices with numerous devices, WiFi 5 may struggle to provide stable speeds and performance.
Support for low-power devices: Older WiFi 5 devices may have limited support, particularly for low-power devices such as IoT devices. This can result in unstable connections or interoperability issues between devices.
Security: Despite introducing some security enhancements, WiFi 5 still has potential vulnerabilities and security risks. This includes potential impacts from vulnerabilities in the WPA2 protocol, making networks susceptible to attacks.
Despite these issues, WiFi 5 remains a widely adopted wireless network standard that can provide reasonable speeds and performance.
4. What makes WiFi 6 superior to WiFi 5?
I won't discuss technical terms like MU-MIMO, OFDMA, MCS (Modulation and Coding Scheme), etc., as they may seem complicated, and even if I were to explain them, you would likely still find it confusing.
Therefore, let's set aside these concepts and explain in plain language why WiFi 6 is powerful.
a、Faster speeds and more device connections
WiFi 6 offers faster internet speeds compared to WiFi 5. This means you can download files, stream videos, and play online games more quickly, providing a smoother online experience.
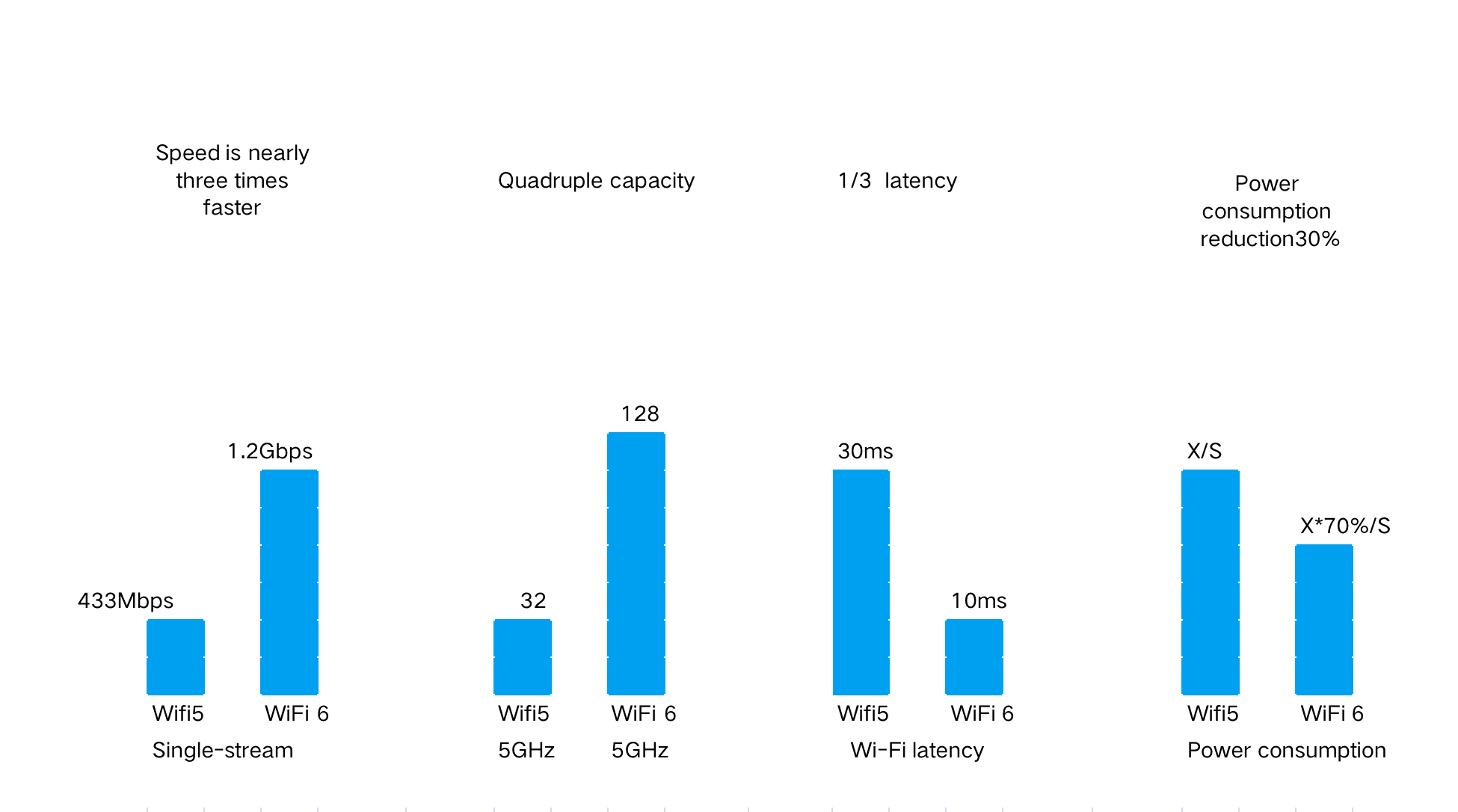
b、The network's transmission efficiency has been improved.
Due to the implementation of OFDMA technology in WiFi 6, the network's transmission efficiency has improved, resulting in reduced network congestion and fewer instances of buffering.
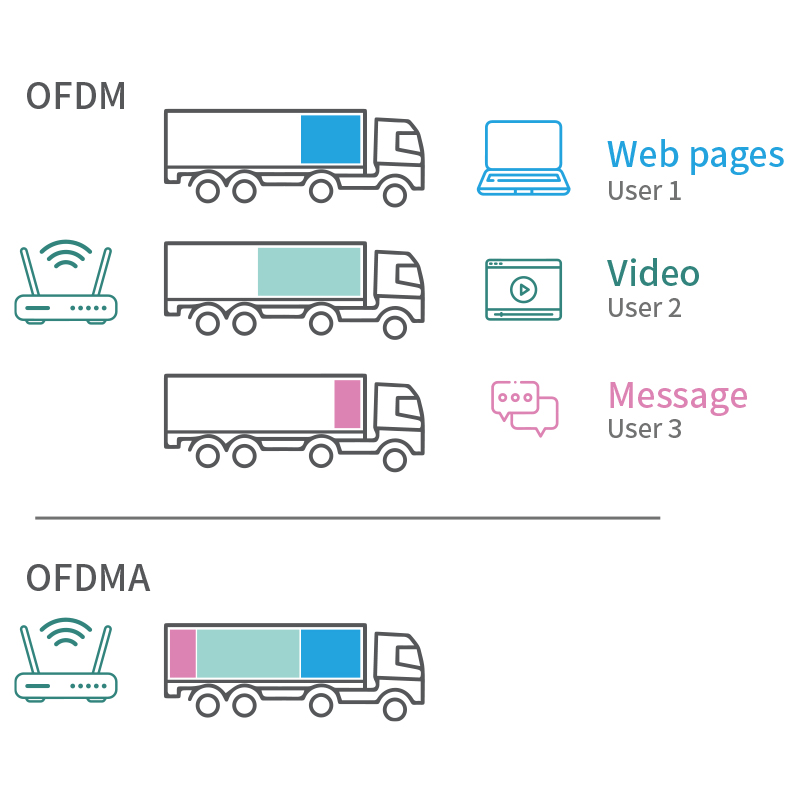
Let's imagine WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 as a fleet of vehicles. With WiFi 5, each vehicle can only deliver data to one customer at a time. For example, if User 1 opens a webpage, User 2 starts streaming a video, and User 3 uses a messaging app, WiFi 5 would need to make three separate trips to deliver data to each user. On the other hand, WiFi 6 can handle all three requests in a single trip.
The greatest benefit of this approach is the reduction of network latency, allowing for smoother network performance.
c、Lower power consumption, more energy-efficient
Currently, WiFi 5 home routers remain operational 24/7, whether or not there are devices connected to them.
However, WiFi 6 introduces on-demand wake-up functionality, meaning it only operates when devices are connected, and goes into a sleep mode when no devices are connected, resulting in lower power consumption.
In simple terms, WiFi 6 builds upon the foundation of WiFi 5 by offering higher performance, faster speeds, and stronger capabilities.
Does this mean you should blindly purchase WiFi 6?
It depends on your specific needs. If you have a lot of devices that require high-speed internet access simultaneously, or if you frequently experience network congestion or performance issues with WiFi 5, then upgrading to WiFi 6 could be beneficial for you. However, if you have few devices and are satisfied with the performance of your current WiFi 5 network, there may not be an urgent need to upgrade.
Consider factors such as the number of devices you have, your internet usage requirements, and your budget before deciding to purchase WiFi 6.
5、Disadvantages of WiFi 6
While WiFi 6 is powerful, it may not be suitable for everyone.
While WiFi 6 offers significant advantages in terms of speed, capacity, and performance, it is important to note that not all individuals or situations may benefit equally from this technology. Factors such as specific needs, device compatibility, budget constraints, and availability of WiFi 6 infrastructure should be considered before deciding to adopt WiFi 6.
a、WiFi 6 has requirements for broadband.
WiFi 6 technology itself does not directly impose specific requirements on the broadband or internet connection. However, to fully utilize the capabilities of WiFi 6, it is recommended to have a high-speed broadband connection. This is because WiFi 6 can deliver faster speeds and accommodate more devices simultaneously, but the actual speed and performance will still depend on the speed and stability of the internet connection provided by your service provider.
If you have a slow or unreliable internet connection, upgrading to WiFi 6 may not significantly improve your overall experience. It is important to ensure that your broadband connection meets the requirements of your internet usage and that your service provider delivers the desired speed and stability.
b、To fully appreciate the advantages of WiFi 6, multiple devices are needed.
In order to fully experience the benefits of WiFi 6, it is recommended to have multiple devices connected to the network. WiFi 6 excels in handling concurrent connections and efficiently managing the traffic from multiple devices simultaneously.
WiFi 6 utilizes technologies like OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) and MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output) to divide the available bandwidth into smaller subchannels and serve multiple devices simultaneously. This allows for improved efficiency, reduced latency, and increased overall network capacity.
If you only have a single device connected to your WiFi network, the advantages of WiFi 6 may not be as pronounced compared to situations where there are numerous devices actively using the network. The true potential of WiFi 6 shines when there is a multitude of devices requiring high-speed connectivity, such as in busy households or environments with many users.
WiFi 6 claims to provide a maximum throughput for the router within a given time frame. For example, when watching a 4K video, a 20 Mbps broadband connection is sufficient, even if you simultaneously use four computers to watch four separate 4K videos, an 80 Mbps connection would still suffice.
So, how many devices are needed to truly experience the advantages of WiFi 6?
WiFi 6 starts to showcase its advantages over WiFi 5 when the number of connected devices exceeds 50. At this point, WiFi 6 tends to outperform WiFi 5 in terms of performance and capacity. This is primarily due to the introduction of OFDMA technology in WiFi 6, which allows for more efficient management and allocation of network resources, reducing congestion and latency.
However, it's important to note that the benefits of WiFi 6 extend beyond just the number of devices. WiFi 6 offers improved throughput, lower latency, and more stable connections. Therefore, when considering an upgrade to WiFi 6, factors such as network congestion, performance requirements, and budget constraints should also be taken into account, in addition to the number of devices.
c、Some devices do not support the WiFi 6 protocol.
It is important to note that not all devices are compatible with the WiFi 6 protocol. WiFi 6 uses the latest wireless standards and technologies, including 802.11ax, which offers significant improvements in speed, capacity, and performance compared to previous WiFi standards like 802.11ac (WiFi 5).
Older devices or devices that only support previous WiFi standards may not be able to take advantage of the full capabilities of WiFi 6. They will continue to operate on their respective supported standards, such as 802.11n (WiFi 4) or 802.11ac (WiFi 5). This means they will not experience the enhanced speeds, lower latency, and improved efficiency that WiFi 6 can provide.
Before upgrading to WiFi 6, it is advisable to check the compatibility of your existing devices. If you have older devices that do not support WiFi 6, you may want to consider whether the benefits of WiFi 6 justify the need for upgrading all your devices. In some cases, it may be more practical to upgrade individual devices to WiFi 6 over time as they become outdated or require replacement.
6、 WiFi 6 and 5G
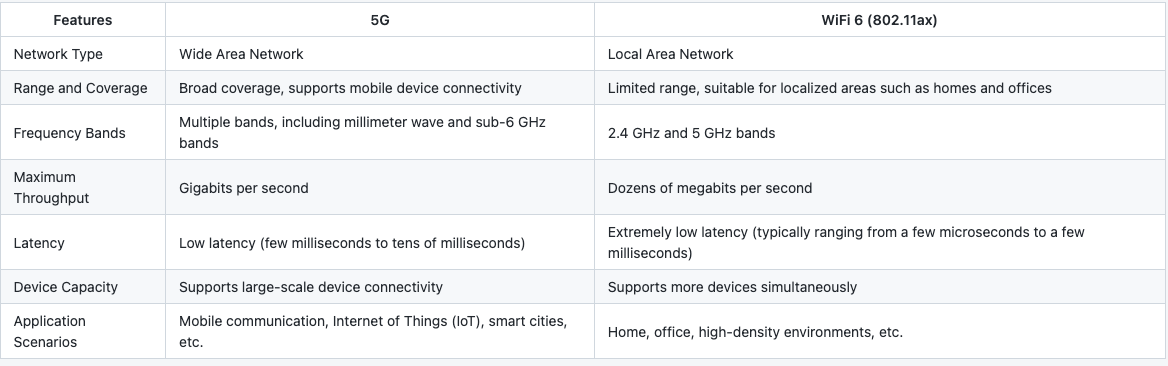
WiFi 6 and 5G are two different wireless communication technologies that provide wireless connectivity solutions in different domains.
WiFi 6 is a wireless technology used for Local Area Networks (LANs), suitable for device connections within homes, offices, and other limited-range environments. It offers faster and more reliable wireless LAN connectivity by providing higher data transfer rates, lower latency, and improved device capacity.
On the other hand, 5G is a Wide Area Network (WAN) mobile communication technology designed to provide high-speed mobile data connectivity for mobile devices and large coverage areas. It offers higher transmission speeds, lower latency, and greater network capacity, catering to the needs of massive connectivity requirements like mobile communications, IoT, and smart cities.
While WiFi 6 and 5G are distinct technologies, they have some overlapping and complementary applications. For instance, in an indoor environment, you can use WiFi 6 to provide high-speed wireless LAN connections, and when you step out of the indoor range into a 5G coverage area, you can switch to 5G for continued high-speed mobile data connectivity.
In summary, WiFi 6 and 5G are wireless communication technologies tailored for different scenarios and needs, enabling various wireless connectivity requirements.
The following table provides a detailed comparison for easy understanding:
6、 Should I buy a WiFi 6 router?
However, if you don't fall into any of these categories or if you are on a limited budget, it ultimately comes down to personal preference. Assess your specific needs, consider your budget, and make a decision accordingly.
Lastly, it is recommended not to buy something too expensive. First, it is important to understand your own needs and not blindly pursue high prices. You should also consider what you can afford. Of course, if cost is not a concern and you are solely focused on excellence, then my advice may not be applicable.
Get the Scoop First
Subscribe to our official website to receive exclusive first-hand news and stay up-to-date on our new product releases and promotions!